Collection: Liquid Handling
Benchtop Equipment & Consumables: Essential Tools for Laboratory Work
-
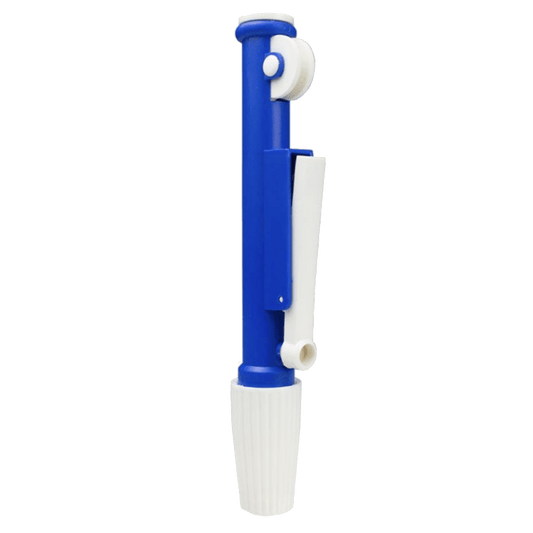
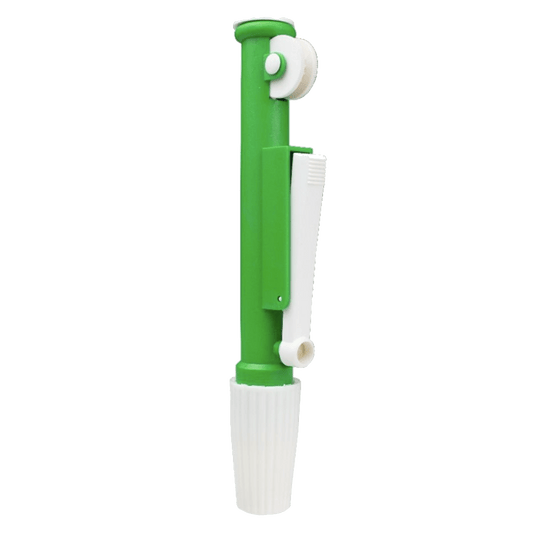
United Scientific Pipette Pumps
Regular price From $113.23 USDRegular priceUnit price / per -
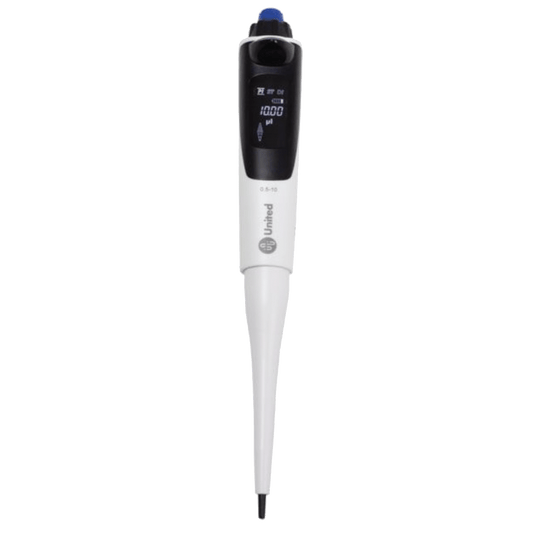
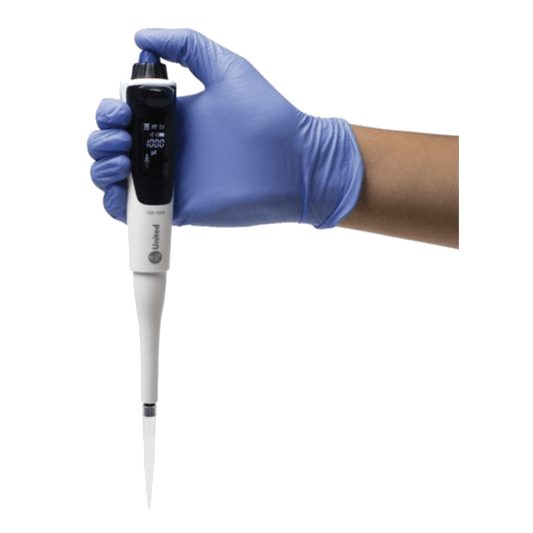
United Scientific Jupiter Electronic Pipettes
Regular price $463.40 USDRegular priceUnit price / per -
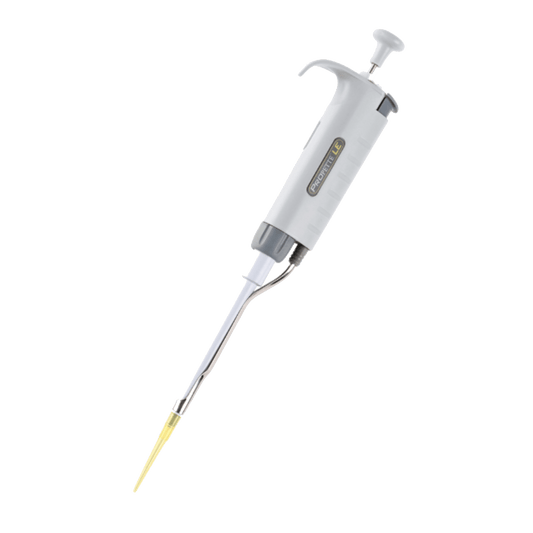
ProPette LE™ Single Channel Pipettors
Regular price $141.75 USDRegular priceUnit price / per -
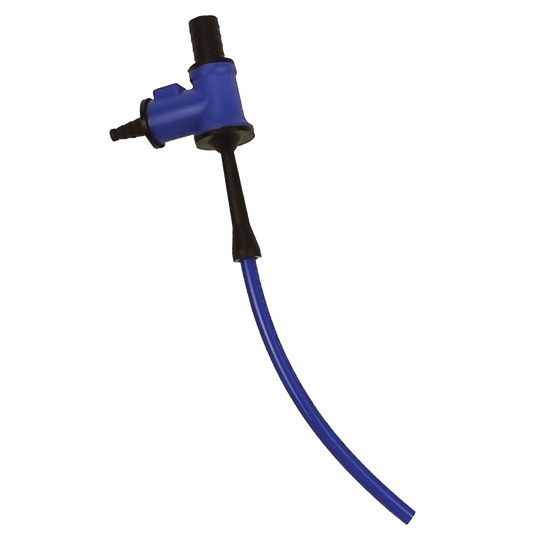
United Scientific Aspirator
Regular price $6.78 USDRegular priceUnit price / per -
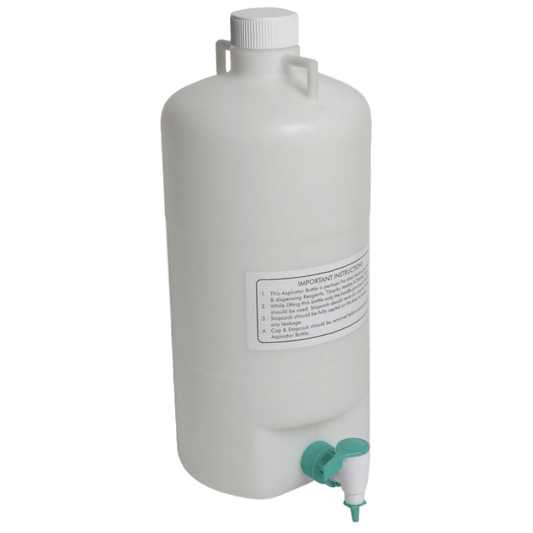
United Scientific Polypropylene Aspirator Bottles
Regular price From $23.31 USDRegular priceUnit price / per -
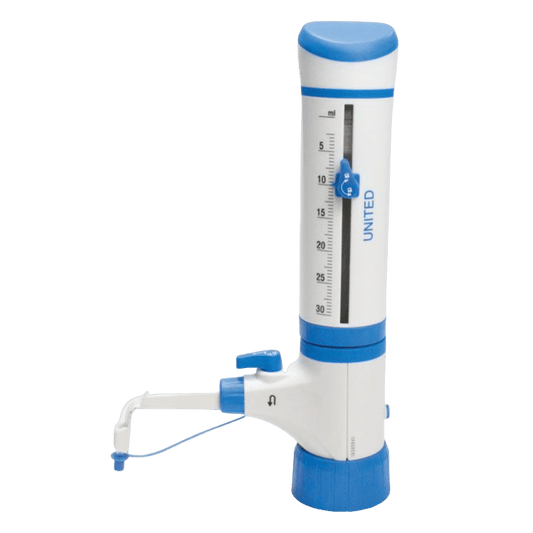
United Scientific Jade Bottle Top Dispensers
Regular price From $350.85 USDRegular priceUnit price / per